
(i) Enzyme immunoassay and chemiluminescence immunoassay IgG/IgM. This review aims to provide a comprehensive summary on the diagnostic tests available for syphilis along with their performance throughout the stages of the disease, including neurosyphilis, and in congenital syphilis. Direct detection methods such as molecular or specialized microscopy techniques are also limited by their performance, availability, and cost. Historically, serology has been the main diagnostic method but continues to have issues with the lack of specificity of nontreponemal tests and a poor correlation of treponemal tests with disease activity. The interpretation of each test varies and depends upon the stage of the disease. The laboratory diagnosis of syphilis, especially in congenital syphilis and neurosyphilis, continues to pose challenges. Neurosyphilis, however, can manifest during any stage of the disease ( 3, 7). When it becomes symptomatic (tertiary), it can involve virtually any organ, including the central nervous system (neurosyphilis), skin, bone (gumma), and the cardiovascular system. The latent stage is divided into early (2 years) and refers to the state where the disease does not manifest any symptoms. pallidum, manifesting frequently as a widespread maculopapular rash and nonspecific systemic symptoms that characterize the secondary stage, which resolves without treatment. It is followed by systemic dissemination of T. Primary syphilis typically presents as a spontaneously resolving painless ulcer (chancre) at the site of inoculation. The natural progression of untreated syphilis is divided into primary, secondary, and latent stages ( 2, – 4, 6, 7). Internationally, >300,000 fetal and neonatal deaths are attributed to syphilis, with an additional 215,000 infants at increased risk of early death ( 5). Globally, there are approximately six million new cases of syphilis annually in persons aged between 15 and 49 years. It is commonly sexually transmitted but can also be vertically transmitted during pregnancy, causing congenital syphilis ( 1, – 4). Syphilis is a multisystem infection caused by Treponema pallidum subsp. It assesses the published literature in this area and makes recommendations for the rational use of pathology testing to aid in the diagnosis of the many facets of syphilis.
#Serological testing chart 4 western blot results update
This review looks at the current status of traditional serological assays and provides an update on more recent methods. As a consequence of this increased incidence of syphilis, there has been interest in the utility of point-of-care tests (POCTs), nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), the role of IgM testing in suspected congenital syphilis, and the laboratory investigation of possible neurosyphilis.

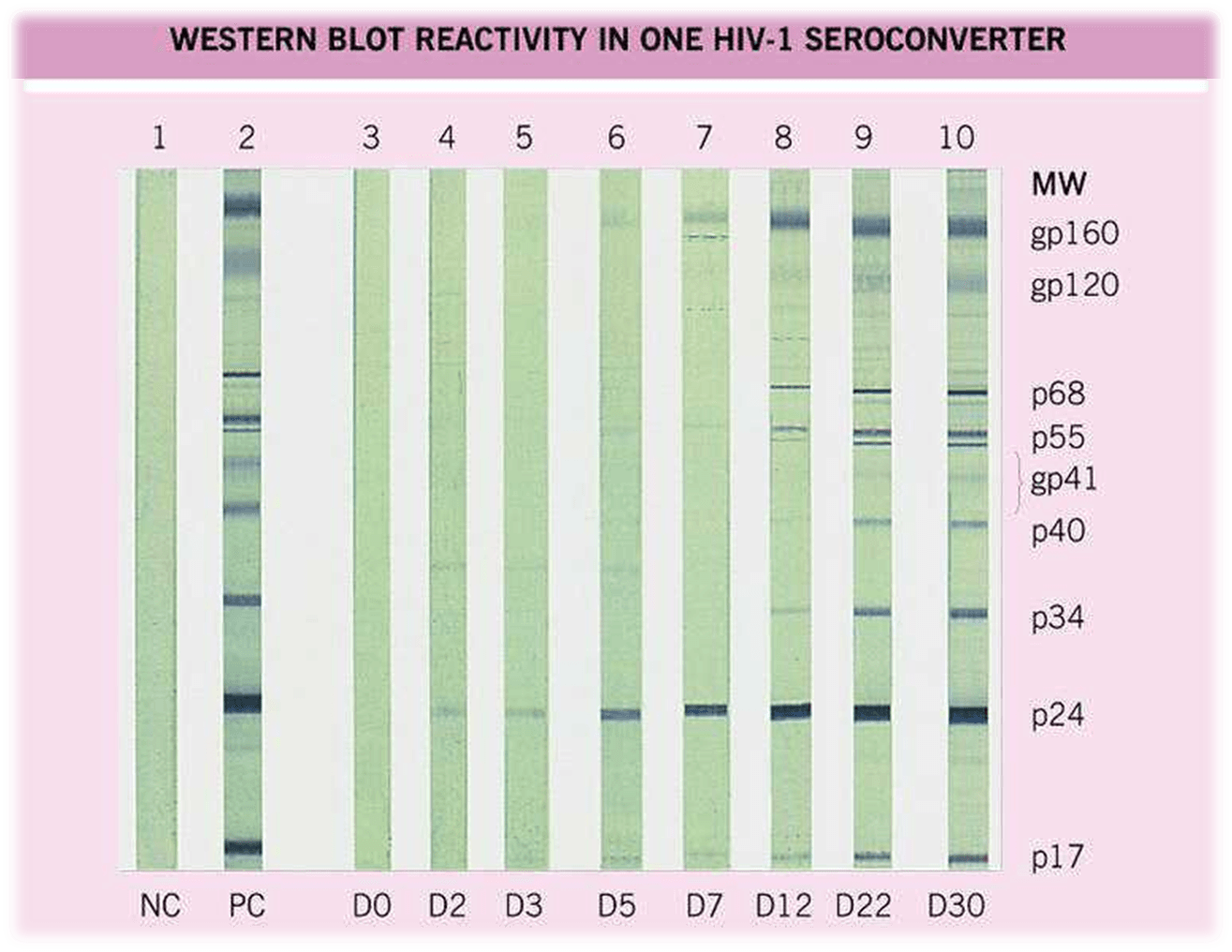
The remoteness of these locations, in conjunction with the particular sociocultural characteristics of the population, pose unique challenges to the traditional diagnostic and treatment paradigms for syphilis. Large foci of infection have been identified in isolated communities. There has been a resurgence of syphilis diagnoses in Australia. The nontreponemal rapid plasma reagin (RPR) flocculation test is used to assess disease activity. pallidum IgG chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) and the T. Currently, cases of possible syphilis are commonly investigated using the treponemal serological tests T. 1 Supplemental or confirmatory tests that are specific enough to distinguish between the falsely positive results of the screening test and the truly positive ones must be used.Syphilis is a multisystem infection caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. This feature means the test has a relatively poor positive predictive value for populations with a low prevalence of HIV infections. Unfortunately, the exquisite sensitivity of the enzyme immunoassay, coupled with less than 100% specificity, creates a potential for falsely positive reactions. Although the enzyme immunoassay for HIV antibodies was originally developed to screen donated blood, it is now routinely used as a diagnostic tool in the workup for HIV infection. THE ACQUIRED immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) epidemic and the increasing concern of both the public and governmental agencies about the testing of low-risk populations for AIDS have created an unprecedented demand for serological testing for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
